Introduction
In a physical environment all
the servers have dedicated physical NIC that are connected to a physical
switch. VLANs in physical world are usually controlled by setting the VLAN ID
on the physical switch port and then setting the server’s IP address to correspond
to that NIC’s VLAN.
But in a virtual environment,
dedicating a physical NIC (pNIC) to each VM that resides on the host is not
possible. In reality, a physical NIC of the Esxi host service many VMs, and
these VM’s may need to be connected to different VLANs. So the method of
setting a VLAN ID on the physical switch port doesn’t work.
To counter this issue, 802.1Q
VLAN tagging comes in picture in virtual environment.
Before digging deep into 802.1Q
VLAN tagging lets understand how networking works in a virtual environment.
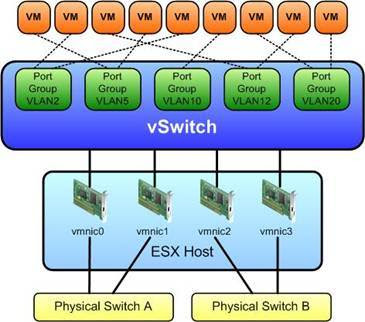
An Esxi host typically can
have more than one physical network adapters for redundancy, load balancing and
segregation. The physical NICs (pNICs) are connected to physical switches and
these pNICs are in turn assigned to vSwitches that are created on
each Esxi host. Connecting pNICs to vSwitches is referred to as uplink
connection. On vSwitch we create different Port groups which can be connected
to the virtual NICs (vNICs) that are assigned to each VM on the host. Virtual
machines can use any pNIC connected to a vSwitch and this is determined by the
load balancing policies which define how pNICs are selected when routing
traffic to and from a VM.
Shown below is a typical
network in a virtual environment.
Using the traditional VLAN
method of assigning a single VLAN ID to a physical NIC does not work very well
in virtual environments because with this method, all the VMs on a vSwitch
would have to use the same VLAN ID. But in most of the cases you need to route
different VM’s through different VLAN’s so the traditional VLAN method is of
less use in this scenario.
Another method which you can
use is to create multiple vSwitches for each VLAN, but if you had many VLANs,
you would need a great number of pNICs and even the modern day servers comes
with limited number of physical network adapters.
To overcome this situation,
802.1Q VLAN tagging is used.
How
802.1Q VLAN tagging for vSphere VLANs works
802.1Q VLAN tagging allows use
of multiple VLANs on a single physical NIC. This capability can greatly reduce
the number of pNICs needed in the host. Instead of having a separate pNIC for
each VLAN, you can use a single NIC to connect to multiple VLANs. Tagging works
by applying tags to all network frames to identify them as belonging to a
particular VLAN.
Types
of 802.1Q VLAN tagging in VMware vSphere
There are several methods for
tagging vSphere VLANs, but they are differentiated by where the tags are
applied. Basically there are 3 types of tagging methods available in Vmware
vSphere. These are explained as below:
1:
Virtual Machine Guest Tagging (VGT)– With this mode, the 802.1Q VLAN trunking driver is
installed inside the virtual machine. All the VLAN tagging is performed by the
virtual machine with use of trunking driver in the guestS. Tags are
understandable between the virtual machine networking stack and external switch
when frames are passed to and from virtual switches. vSwitch only forwards the
packets from Virtual machine to physical switch and will not perform any
operation.
Prerequisite
for configuring VGT
1) Port group of the virtual machine should be configured with VLAN ID 4095.
1) Port group of the virtual machine should be configured with VLAN ID 4095.
2) The physical switch port
connecting the uplink from the Esxi server should be configured as Trunk port.
How
to configure VGT
To configure VGT
login into your guest O.S and select the network adapter for which you want to configure
tagging. Open the properties of this adapter and click on configure in the popup window which opens. In
the next window select the advance tab and select VLAN from list of
configurable options and specify the VLAN ID through which traffic of this
adapter needs to pass.
2:
External Switch Tagging (EST) –
In this mode, physical switches does the VLAN tagging. The tag is appended when
a packet arrives at a switch port and stripped away when a packet leaves a
switch port toward the server.
Since the tagging is done at
physical switch so virtual switch have no information of this and you do not
need to configure any VLAN at portgroup level. VM network Packet is delivered
to physical switch without any tagging operation performed at virtual switch
level.
Note: There is one caveat in this
approach. You can only create those many numbers of VLAN’s equal to number of
physical NIC’s present/connected to your Esxi host.
Prerequisites
for Configuring EST
1) Number of physical NIC’s =
no of VLANs connected to ESX
2) The physical switch port
connecting the uplink from the ESX should be configured as Access port assigned
to specific VLAN.
Virtual
Switch Tagging (VST) –
In this mode, VLANs are configured on port groups of the virtual switch. The
vNIC of the virtual machine is then connected to the appropriate port group.
The virtual switch port group tags all outbound frames and removes tags for all
inbound frames.
This approach reduces the
number of Physical NIC’s on the server by running all the VLANs over one physical
NIC. Since less physical NIC’s are used, it also reduces the number of cables
from Esxi host to physical switch.
Best practice is to use NIC
teaming and keep 2 NIC’s for redundancy.
Prerequisite
for configuring VGT
The physical switch port
connecting the uplink from the ESX should be configured as Trunk port.
VST mode is the one that is
most commonly used for configuring VLANs in vSphere because it’s easier to
configure and manage. It also eliminates the need to install a specific VLAN
driver inside a virtual machine, and there is almost no performance impact from
doing the tagging inside the virtual switches.
You can consult the below table
to determine which will be the best tagging policy in your environment






Comments
Post a Comment